

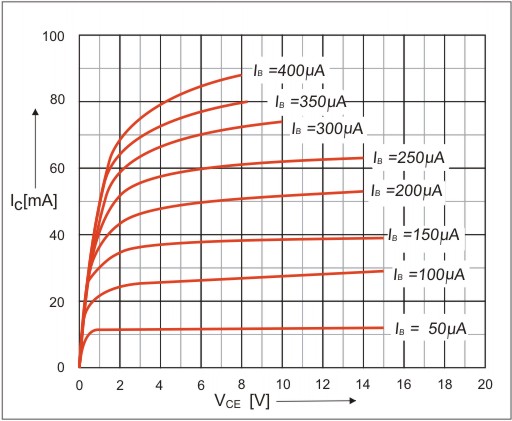
ApplicationĪs previously mentioned, a BC547 amplifies a current’s collector-base voltage. Then, the voltage’s measurement is in V BE.Īs a result of this stage, and the fact that it is the cut-off region, the base voltage can reach 660 mV. Typically, the emitter voltages allowed across the collector are 200 mV and 900mV on the base. Electric enthusiasts term this the Saturation Region, and the flow is across the collector and emitter. Once your silicon transistor’s bias is to its total capacity, a max of 100mA can flow from across the collector and emitter. However, the value should not exceed 5mA. Moreover, if you wish to bias a transistor, you can add a base terminal pin. As for the maximum amount? The flow through the collector-base pin can only reach a max of 100mA. Typically, the BC547 has an amplification capacity of 110 to 800. Let’s dive into more details about the transistor. Also, 5mA is the maximum Base Current (I B).Ī circuit board with its electrical components, including a transistor.Then, it has a continuous Collector current (I C) of 100mA.Secondly, its DC Current Gain (h FE) is at a maximum of 800.That current needs to go somewhere, and therefore, it drains out of the emitter.

The base controls the biasing of the transistor.
Here, the current’s job is to flow through the collector pin. Wondering what the BC547 transistor’s pinout configuration is? Here is everything you need to know: We’ll discuss this in more detail later, but usually, you’ll place this type of transistor after a circuit’s load. When applying power to the control pin/ base terminal, the energy will flow from the collector to the emitter. What is a BC547 Transistor?Ī BC547 is a type of NPN. If you’re into electrics, you’ll already know that the flow of electrons makes this process work.Ī diagram of the BC547. These three sections are an emitter, base, and collector. What is an NPN Transistor?Īn NPN Transistor (or negative-positive-negative transistor) is a general-purpose transistor used for signal amplification.įurthermore, like most transistors, an NPN has three layers controlled by a collector current. For this reason, it is a common base amplifier. Why is that? The power between the emitter and collector can easily be higher than the base. Likewise, you may also be familiar with the terms transistor and amplifier in one sentence. Often, triggering the base current allows the emitter and collector to connect, thereby forming a switching element. In technical terms, we have the input as emitter, the output as a collector, and the control line as the base. In a nutshell, it is an electrically controlled switch.įor this specific switch to work, it requires input, output, and a control line.
BC547 TRANSISTOR PINOUT DRIVER
It is especially crucial if you’ll be working with driver modules, amplifier modules, or Darlington pairs. So, are you ready to learn more about these fascinating electronic components? Let’s get started! What Is A Transistor?īefore we jump into what a BC547 transistor is, let’s cover what a transistor is. The BC547 is a necessary transistor to know and understand as a switch or an amplifier. Are you interested in learning more about the topic? You’ve come to the right place! Here, we will be discussing all that there is to know about the BC547 transistor. If you’re an electric enthusiast, the chances are that you’ll come across a BC547 in one way another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
